Written by KRITIKA SINHA | MARKETING
Imagine launching your startup after months of hard work, only to wake up to a data breach that exposes sensitive customer information. Not only is your business’s reputation at risk, but you could also face financial and legal consequences. Cybercriminals increasingly target startups, assuming they lack the robust security measures of larger enterprises. A report by Verizon states that 43% of cyberattacks target small businesses, with many falling victim due to inadequate security practices.
This blog will discuss why penetration testing for startups is critical, the common threats new businesses face, and how a proactive security approach can safeguard your growth. We’ll also explore how Transputec provides tailored penetration testing solutions for startups, ensuring your business remains resilient against cyber threats.
What Is Penetration Testing?
Penetration testing, often called pen testing, is a crucial cybersecurity practice where skilled professionals simulate cyberattacks on an organisation’s digital assets. This controlled and authorised process aims to uncover vulnerabilities in systems, networks, and applications before malicious hackers can exploit them. By mimicking real-world attack scenarios, pen testers probe for weaknesses using sophisticated tools and techniques, much like those employed by cybercriminals.
Transputec offers comprehensive penetration testing services. Our team of experienced cybersecurity experts and certified ethical hackers employs cutting-edge tools and techniques to thoroughly test your systems, networks, and applications.
What Is Penetration Testing for Startups?
Penetration testing, or ethical hacking, is a cybersecurity process where security professionals simulate real-world cyberattacks on your startup’s systems, networks, and applications. The goal is to identify vulnerabilities before malicious hackers exploit them. Startups are particularly vulnerable due to limited security budgets, rapid digital transformation, and reliance on cloud-based services.
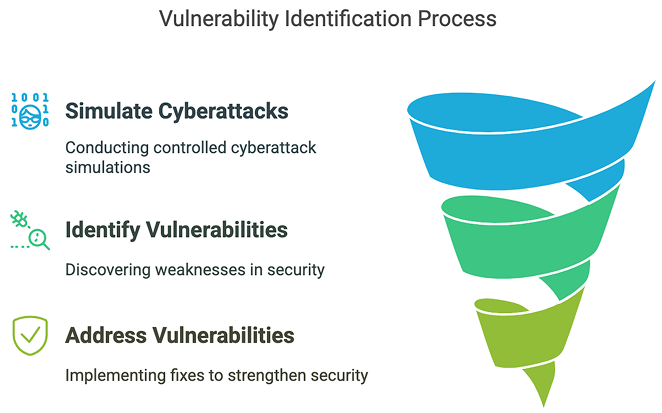
Benefits of Penetration Testing for Startups
1. Building a Security-First Culture
Instilling the importance of security from the outset sets a precedent for all future development and operations, emphasising that security and innovation go hand in hand.
2. Attracting Investment
Demonstrating a commitment to security through rigorous penetration testing can make a startup more appealing to potential investors who are reassured by proactive risk management practices.
3. Accelerating Market Entry
By identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities early, startups can avoid delays associated with security breaches, ensuring a smoother and faster path to market.
3. Compliance with Regulations
Penetration testing helps startups meet industry regulations such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, SOC 2, and GDPR, minimising the risk of non-compliance fines and data breaches.
4. Enhancing Customer Trust
Regular penetration testing demonstrates a proactive approach to security, building trust with customers and positioning your startup as a reliable partner.
Ensure your Startup’s Security from Day One and Build a Resilient Future.
Contact us today to connect with an expert and get started on optimising your IT operations.
Why Startups Are Prime Targets for Cyber Attacks?
Startups are prime targets for cyberattacks due to several critical factors that make them attractive to cybercriminals. Here’s why startups often find themselves in the crosshairs of hackers:
1. Lack of Robust Security Measures
Many startups operate with limited budgets and prioritise growth over cybersecurity. This means they may lack dedicated IT security teams, fail to implement strong security protocols, and rely on default security settings, making them easy prey for cybercriminals.
2. Valuable Data with Weak Protection
Startups handle sensitive customer data, intellectual property, and financial information. However, without proper encryption, firewalls, or access controls, this data becomes an easy target for attackers looking to steal or sell it on the dark web.
3. Use of Cloud-Based Solutions
Startups often rely on cloud services to reduce operational costs. However, misconfigured cloud storage, weak access controls, and insecure APIs can leave systems exposed to unauthorised access, leading to data breaches.
4. Rapid Digital Expansion
Due to fast-paced growth, startups frequently launch new applications, websites, and integrations. These new digital assets often go live without thorough security testing, increasing the attack surface for cyber threats.
5. Lack of Cybersecurity Awareness
Employees in startups may not receive adequate cybersecurity training, making them susceptible to phishing attacks, weak password practices, and social engineering tactics. According to the Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, 85% of breaches involve human error.
6. Third-Party Risks
Startups often partner with third-party vendors for development, marketing, or payment processing. If these vendors have weak security, attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in supply chain attacks to gain access to the startup’s infrastructure.
7. Target for Ransomware & Extortion Attacks
Hackers assume that startups lack sophisticated backup and recovery plans. Ransomware attackers encrypt crucial business files and demand payment to restore them, knowing that startups are more likely to pay to avoid downtime.
8. Regulatory Compliance Risks
Many startups operate in industries with strict compliance requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS. Non-compliance due to security lapses can result in legal action, fines, and loss of customer trust.
How Transputec Provides Penetration Testing for Startups
At Transputec, we specialise in helping startups strengthen their cybersecurity posture with our expert-led penetration testing for startup services. Our process includes:
1. Comprehensive Security Assessment
We analyse your IT infrastructure, applications, and networks to identify vulnerabilities that hackers could exploit.
2. Real-World Attack Simulations
Our ethical hackers simulate actual cyberattacks, testing your startup’s resilience against various threats, including phishing, SQL injections, and malware.
3. Detailed Reporting & Risk Prioritisation
After testing, we provide an in-depth report outlining security flaws, their risk levels, and actionable recommendations for remediation.
4. Remediation Support & Re-Testing
Unlike one-time testing, we assist in fixing vulnerabilities and conduct re-testing to ensure your startup remains secure.
5. Continuous Security Monitoring
Cyber threats evolve, and so should your security. We offer ongoing monitoring to keep your startup protected at all times.
Conclusion
Startups operate in a fast-paced environment where cybersecurity often takes a backseat—until a breach occurs. Penetration testing for startups is an essential security measure, helping businesses detect vulnerabilities before they are exploited. Whether you’re launching a new product, scaling operations, or handling sensitive customer data, penetration testing can safeguard your startup from cyber threats.
At Transputec, we provide comprehensive penetration testing for startups, tailored to your unique business needs. Our security experts help you identify, mitigate, and prevent cyber risks, ensuring your startup stays resilient in today’s threat landscape.
Ready to secure your startup? Contact us today to connect with an expert and get started with Transputec!

Secure Your Business!
Ready to explore how we can enhance your security posture? Contact us today to speak with one of our experts.
FAQs
1. Why is penetration testing for startups important?
Penetration testing for startups is essential because startups are frequent targets of cyberattacks. It helps identify security vulnerabilities before hackers can exploit them, preventing financial losses, legal penalties, and reputational damage.
2. How often should a startup conduct penetration testing?
Startups should conduct penetration testing at least once a year or whenever there are significant system updates, product launches, or regulatory compliance requirements.
3. Does Transputec offer customised penetration testing for startups?
Yes, Transputec provides tailored penetration testing for startups, considering factors like business size, industry regulations, and technology stack to deliver the most effective security solutions.
4. How does penetration testing help startups meet compliance requirements?
Many compliance regulations, such as GDPR and ISO 27001, require businesses to conduct security assessments. Penetration testing for startups helps ensure compliance, avoiding potential legal penalties.
5. How can I get started with penetration testing for my startup?
You can contact Transputec to discuss your startup’s security needs. Our experts will guide you through the penetration testing process and help you strengthen your cybersecurity defenses.